sim3d.Light
Description
Use the sim3d.Light object to create an actor object with
N number of light elements in the 3D environment for custom lighting.
After you create a sim3d.Light object, you can modify aspects of the light
actor by setting property values.
Creation
Description
light = sim3d.Light()
light = sim3d.Light(Name=Value)NumberOfLights to
3.
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments as
Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is
the argument name and Value is the corresponding value.
Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the
pairs does not matter.
Example: light = sim3d.Light(ActorName='Light',Translation=[3 4 3],Rotation=[0
pi/2 -pi/4]) creates an actor object with one light element at the specified
position.
Example: lights =
sim3d.Light(ActorName='Lights',NumberOfLights=3,LightType='PointLight',Translation=[27
-15 0; 27 0 4; 27 15 -2],Rotation=[0 0 0; 0 -pi/2 0; 0 -pi/2 0]) creates an
actor object with three light elements of the type point light at the specified positions.
You cannot see the light actors themselves, but their effects on nearby surfaces are
visible.
Name of actor, specified as a character array or string. If you do not specify an actor name,
then the software assigns the actor an autogenerated name. Use
this argument to set the name of the
sim3d.Light object.
Note
If you specify the same name as an actor that already exists, then the software appends actor name you specify with a unique identifier.
Total number of lights, specified as a real positive scalar. Use this argument to create N number of light elements in the 3D environment.
Example: NumberOfLights=3
Data Types: double
Type of light, specified as 'PointLight',
'SpotLight', 'RectLight', or
'DirectionalLight'. Use this argument to simulate various
lighting effects.
| Light Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Example: LightType='SpotLight'
Data Types: string
Relative translation
(x,y,z) of the actor object to its
parent actor, specified as a real N-by-3 array, in m. N
specifies the number of elements created using the sim3d.Light object. When
you add an actor to the 3D environment, the default parent actor is the Scene
Origin at (0,0,0).
Example: Translation=[3 4 3]
Example: Translation=[0 -1 0; 0 0 0; 0 1 0]
Data Types: double
Relative rotation (roll, pitch, yaw) of the actor object to its parent actor, specified as a real N-by-3 array, in rad.
Example: Rotation=[0 pi/2 -pi/4]
Example: Rotation=[0 pi -pi/2; 0 pi -pi/2; 0 pi
-pi/2]
Data Types: double
Type of actor mobility to respond to physics, move the actor
during simulation, or both, specified as 'sim3d.utils.MobilityTypes.Movable'
or 'sim3d.utils.MobilityTypes.Static'. When you set the
Mobility to 'sim3d.utils.MobilityTypes.Movable', all
the properties become run-time configurable, allowing for programmatic interaction. For more
details on programmatic interaction, see Programmatic Interaction.
Example: Mobility =
sim3d.utils.MobilityTypes.Movable
Data Types: sim3d.utils.MobilityTypes
Output Arguments
Actor object, returned as a sim3d.Light object.
Properties
All the properties are run-time configurable and can also be used for programmatic
interaction during simulation when the Mobility is set to
'sim3d.utils.MobilityTypes.Movable'.
Base Attributes
Parent of actor, specified as a handle to the parent actor object. After you add an actor to
the sim3d.World object, the default parent actor is the
Scene Origin at (0,0,0). Use this property to
set any actor in the 3D environment as the parent actor of a
sim3d.Light object.
This property is read-only.
Children of actor, specified as a structure.
Each field of the structure contains a handle to
the child of a sim3d.Light
object.
Parent world, specified as a handle to the parent sim3d.World
object. You can use this property only if the sim3d.Light object is
added to the parent sim3d.World object.
Coordinate system that the actor uses for translation and rotation in the 3D environment, specified as one of these listed values:
'Default'– World coordinate system'MATLAB'– MATLAB® coordinate system'ISO8855'– ISO 8855 standard coordinate system'AERO'– SAE coordinate system'VRML'– X3D ISO standard coordinate system'SAE'– SAE coordinate system
For more details on the different coordinate systems, see Coordinate Systems in Simulink 3D Animation.
Data Types: string
Relative translation
(x,y,z) of the actor object to its
parent actor, specified as a real N-by-3 array, in m. N
specifies the number of elements created using the sim3d.Light object. When
you add an actor to the 3D environment, the default parent actor is the Scene
Origin at (0,0,0).
Example: light.Translation = [1 2 1]
Example: lights.Translation = [1 4 2; 1 3 2; 1 2
2]
Relative rotation (roll, pitch, yaw) of the actor object to its parent actor, specified as a real N-by-3 array, in rad.
Example: light.Rotation = [0 pi/2 pi/8]
Example: lights.Rotation = [pi/2 pi/4 pi/2; 0 pi/4 pi/2; pi pi/2
0]
Type of actor mobility to respond to physics, move the actor
during simulation, or both, specified as 'sim3d.utils.MobilityTypes.Movable'
or 'sim3d.utils.MobilityTypes.Static'. When you set the
Mobility to 'sim3d.utils.MobilityTypes.Movable', all
the properties become run-time configurable, allowing for programmatic interaction. For more
details on programmatic interaction, see Programmatic Interaction.
Example: light.Mobility =
sim3d.utils.MobilityTypes.Movable
Data Types: sim3d.utils.MobilityTypes
Status of light in the 3D environment, specified as 1
(true) to turn on the light or 0
(false) to turn off the light. For N number of
lights, specify as a logical N-by-1 vector.
Example:
light.LightState = 1
Example:
lights.LightState = [1; 1; 1]
Data Types: logical
Color of light, specified as real N-by-3 array of RGB triplet values. An RGB triplet is a three-element row vector whose elements specify the intensities of the red, green, and blue components of the color. The intensities must be in the range [0, 1].
Example: light.LightColor = [ 0.5 0.7 0.4]
Example: lights.LightColor = [ 1 0 0; 0 1 0; 0 0
1]
Data Types: double
Brightness of light, specified as real positive N-by-1 vector.
Example: light.Intensity = 4000
Example: lights.Intensity = [4500; 4500; 4500]
Data Types: double
Light intensity unit name, specified as 'Lumens', or
'Candelas'. The default value for this property is an empty
string ' '.
Example: light.IntensityUnit = 'Lumens'
Example: lights.IntensityUnit = ['Candelas'; 'Candelas';
'Candelas']
Dependencies
This property cannot be set when LightType is
'DirectionalLight'
Data Types: string
Range of light, specified as real positive N-by-1 vector, in m. Use this property to reduce computational load by limiting illumination to necessary areas of the environment.
Example: light.AttenuationRadius = 20
Example: lights.AttenuationRadius = [30; 35; 40]
Dependencies
This property cannot be set when LightType is
'DirectionalLight'
Data Types: double
Temperature of emitted light, specified as real positive N-by-1 vector, in K. As temperature value increases, the appearance of the light changes from a warmer tone to a cooler tone.
Example: light.Temperature = 4500
Example: lights.Temperature = [6000; 6000; 6000]
Data Types: double
Source file for IES texture, specified as string N-by-1array. After you import an IES texture file you can modify other aspects of the light by setting additional properties.
Note
If you import an IES texture file, LightType does not
impact the light actor.
Example: light.IESFilePath =
fullfile(pwd,"file.ies")
Example: lights.IESFilePath =
fullfile(pwd,["file.ies";"file.ies";"file.ies"])
Data Types: string
Source file for projection, specified as a string N-by-1array. The supported file types are JPEG, PNG, and BMP. The file path should be absolute. This property allows you to project a pattern, texture, or image onto surfaces using the light source as a projector. You can set additional properties to modify other aspects of the light.
Example: light.LightFunction =
fullfile(pwd,"file.jpg")
Example: lights.LightFunction =
fullfile(pwd,["file.jpg";"file.jpg";"file.jpg"])
Dependencies
Set the Mobility property to
sim3d.utils.MobilityTypes.Movable.
Data Types: string
Projection scale, specified as a real N-by-3 array. This property adjusts the overall size of the projection along the X, Y, and Z axes. Use this property to make the projected content larger or smaller in relation to the projection surface.
Example: light.LightFunctionScale = [2 2 2]
Example: lights.LightFunctionScale = [2 2 2; 2 2 2; 2 2
2]
Data Types: double
Point Light Attributes
Radius of light source, specified as real positive N-by-1 vector, in m. A larger value creates a diffused spherical light. A smaller value creates a focused spherical light.
Example: light.SourceRadius = 0.5
Example: lights.SourceRadius = [0.5; 0.4; 0.3]
Dependencies
Set LightType to 'PointLight'.
Data Types: double
Length of light source along the Z axis, specified as real positive N-by-1 vector, in m. A larger value spreads the light over a longer area. A smaller value creates a directional light.
Example: light.SourceLength = 1
Example: lights.SourceLength = [2; 2; 2]
Dependencies
Set LightType to 'PointLight'.
Data Types: double
Spot Light Attributes
Angle of light beam, specified as real positive N-by-1 vector, in deg. This property represents the angle between the center axis of the spot light and the outer edge of the light cone.
Example: light.ConeAngle = 30
Example: lights.ConeAngle = [25; 25; 25]
Dependencies
Set LightType to 'SpotLight'.
Data Types: double
Rectangular Light Attributes
Width of rectangular light source along the Y axis, specified as real positive N-by-1 vector, in m. A larger value provides a wide light source with a broad coverage area. A smaller value provides a narrow light source with focused illumination.
Example: light.SourceWidth = 0.7
Example: lights.SourceWidth = [0.8; 0.8; 0.8]
Dependencies
Set LightType to 'RectLight'.
Data Types: double
Height of rectangular light source along the Z axis, specified as real positive N-by-1 vector, in m. A larger value provides a taller light source with a larger coverage area. A smaller value provides a shorter light source with focused illumination.
Example: light.SourceHeight = 0.7
Example: lights.SourceHeight = [0.8; 0.8; 0.8]
Dependencies
Set LightType to 'RectLight'.
Data Types: double
Examples
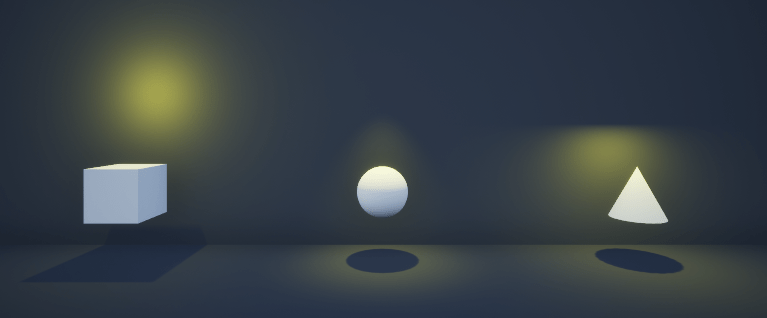
Create custom lighting using a sim3d.Light object in the 3D environment. First, create a room. Next, create and place three actors inside the room. Then, create a point light, a spot light, and a rectangular light and place them above each actor inside the room. Finally, view the room and the actors illuminated by the different types of light in the Simulation 3D Viewer window.
Create 3D Environment
Create a world object using sim3d.World.
world = sim3d.World();
Create Room
Create a room using the sim3d.Actor object. Set the properties of the room to visualize the light and add the room to the world.
room = sim3d.Actor(ActorName='Room'); createShape(room,'box',[60 60 20]); room.Shadows = 1; room.TwoSided = 1; room.Flat = 1; room.Metallic = 0; room.Shininess = 0; room.Color = [0.1 0.1 0.1]; add(world,room);
Create Actors
Create actors inside the room using the sim3d.Actor object. Set the properties of the actors and add the actors to the world.
% Create box actor box = sim3d.Actor(ActorName='Box'); createShape(box,'box',[3 3 3]); box.Translation = [27 -15 -6]; box.Shadows = 1; box.Metallic = 0; box.Shininess = 0; add(world,box); % Create sphere actor sphere = sim3d.Actor(ActorName='Sphere'); createShape(sphere,'sphere',[3 3 3]); sphere.Translation = [27 0 -6]; sphere.Shadows = 1; sphere.Metallic = 0; sphere.Shininess = 0; add(world,sphere); % Create cone actor cone = sim3d.Actor(ActorName='Cone'); createShape(cone,'cone',[3 3 3]); cone.Translation = [27 15 -6]; cone.Shadows = 1; cone.Metallic = 0; cone.Shininess = 0; add(world,cone);
Create Point Light
Create a point light, set the light properties, and place the light above the box actor.
pointlight = sim3d.Light( ... ActorName='PointLight', ... LightType='PointLight'); pointlight.SourceRadius = 0.5; pointlight.Intensity = 50000; pointlight.AttenuationRadius = 20; pointlight.Translation = [27 -15 0]; pointlight.LightColor = [1 1 0]; add(world,pointlight);
Create Spot Light
Create a spot light, set the light properties, and place the light above the sphere actor.
spotlight = sim3d.Light( ... ActorName='SpotLight', ... LightType='SpotLight'); spotlight.Intensity = 500000; spotlight.Translation = [27 0 4]; spotlight.Rotation = [0, -pi/2, 0]; spotlight.AttenuationRadius = 20; spotlight.LightColor = [1 1 0]; spotlight.ConeAngle = 30; add(world,spotlight);
Create Rectangular Light
Create a rectangular light, set the light properties, and place the light above the cone actor.
rectlight = sim3d.Light( ... ActorName='RectLight', ... LightType='RectLight'); rectlight.Intensity = 50000; rectlight.Translation = [27 15 -2]; rectlight.Rotation = [0, -pi/2, 0]; rectlight.AttenuationRadius = 20; rectlight.LightColor = [1 1 0]; rectlight.SourceWidth = 3; add(world,rectlight);
Run Simulation
Set the Simulation 3D Viewer window point of view and run the simulation. You can visualize the reflections of each light type on the wall behind the actors.
viewport = createViewport(world,Translation=[3 0 -2]); sampletime = 0.01; stoptime = 5; run(world,sampletime,stoptime);
delete(world);
Version History
Introduced in R2024aThe sim3d.Light object has DirectionalLight as
LightType. Use this light source to illuminate all the objects in the
scene equally.
The sim3d.Light object has these base attributes:
MobilityLightFunctionLightFunctionScale
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)



