oobLoss
Out-of-bag classification loss for bagged classification ensemble model
Description
L = oobLoss(ens)L for the out-of-bag data in the bagged classification
ensemble model ens. The interpretation of
L depends on the loss function
(LossFun). In general, better classifiers yield
smaller classification loss values. The default LossFun
value is "classiferror" (misclassification rate in
decimal).
L = oobLoss(ens,Name=Value)
Examples
Load Fisher's iris data set.
load fisheririsGrow a bag of 100 classification trees.
ens = fitcensemble(meas,species,'Method','Bag');
Estimate the out-of-bag classification error.
L = oobLoss(ens)
L = 0.0400
Input Arguments
Bagged classification ensemble model, specified as a ClassificationBaggedEnsemble model object trained with fitcensemble.
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments as
Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is
the argument name and Value is the corresponding value.
Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the
pairs does not matter.
Before R2021a, use commas to separate each name and value, and enclose
Name in quotes.
Example: oobLoss(ens,Learners=[1 2 3 5],UseParallel=true)
specifies to use the first, second, third, and fifth learners in the
ensemble, and to perform computations in parallel.
Indices of the weak learners in the ensemble to use with
oobLoss, specified as a
vector of positive integers in the range
[1:ens.NumTrained]. By default,
the function uses all learners.
Example: Learners=[1 2 4]
Data Types: single | double
Loss function, specified as a built-in loss function name or a function handle.
The following table describes the values for the built-in loss functions.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
"binodeviance" | Binomial deviance |
"classifcost" | Observed misclassification cost |
"classiferror" | Misclassified rate in decimal |
"exponential" | Exponential loss |
"hinge" | Hinge loss |
"logit" | Logistic loss |
"mincost" | Minimal expected misclassification cost (for classification scores that are posterior probabilities) |
"quadratic" | Quadratic loss |
"mincost"is appropriate for classification scores that are posterior probabilities.Bagged and subspace ensembles return posterior probabilities by default (
ens.Methodis"Bag"or"Subspace").To use posterior probabilities as classification scores when the ensemble method is
"AdaBoostM1","AdaBoostM2","GentleBoost", or"LogitBoost", you must specify the double-logit score transform by entering the following:ens.ScoreTransform = "doublelogit";For all other ensemble methods, the software does not support posterior probabilities as classification scores.
You can specify your own function using function handle notation. Suppose that
n is the number of observations in X, and
K is the number of distinct classes
(numel(ens.ClassNames), where ens is the input
model). Your function must have the signature
lossvalue = lossfun(C,S,W,Cost)The output argument
lossvalueis a scalar.You specify the function name (
lossfun).Cis ann-by-Klogical matrix with rows indicating the class to which the corresponding observation belongs. The column order corresponds to the class order inens.ClassNames.Create
Cby settingC(p,q) = 1, if observationpis in classq, for each row. Set all other elements of rowpto0.Sis ann-by-Knumeric matrix of classification scores. The column order corresponds to the class order inens.ClassNames.Sis a matrix of classification scores, similar to the output ofpredict.Wis ann-by-1 numeric vector of observation weights. If you passW, the software normalizes the weights to sum to1.Costis a K-by-Knumeric matrix of misclassification costs. For example,Cost = ones(K) - eye(K)specifies a cost of0for correct classification and1for misclassification.
For more details on loss functions, see Classification Loss.
Example: LossFun="binodeviance"
Example: LossFun=@Lossfun
Data Types: char | string | function_handle
Aggregation level for the output, specified as "ensemble",
"individual", or "cumulative".
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
"ensemble" | The output is a scalar value, the loss for the entire ensemble. |
"individual" | The output is a vector with one element per trained learner. |
"cumulative" | The output is a vector in which element J is
obtained by using learners 1:J from the input
list of learners. |
Example: Mode="individual"
Data Types: char | string
Flag to run in parallel, specified as a numeric or logical 1
(true) or 0 (false). If you specify
UseParallel=true, the oobLoss function executes
for-loop iterations by using parfor. The loop runs in parallel when you have Parallel Computing Toolbox™.
Example: UseParallel=true
Data Types: logical
More About
Bagging, which stands for “bootstrap aggregation,”, is a
type of ensemble learning. To bag a weak learner such as a decision tree on a data set,
fitcensemble generates many bootstrap
replicas of the data set and grows decision trees on these replicas. fitcensemble obtains each bootstrap replica by randomly selecting
N observations out of N with replacement, where
N is the data set size. To find the predicted response of a trained
ensemble, predict take an average over predictions from
individual trees.
Drawing N out of N observations
with replacement omits on average 37% (1/e) of
observations for each decision tree. These are "out-of-bag" observations.
For each observation, oobLoss estimates the out-of-bag
prediction by averaging over predictions from all trees in the ensemble
for which this observation is out of bag. It then compares the computed
prediction against the true response for this observation. It calculates
the out-of-bag error by comparing the out-of-bag predicted responses
against the true responses for all observations used for training.
This out-of-bag average is an unbiased estimator of the true ensemble
error.
Classification loss functions measure the predictive inaccuracy of classification models. When you compare the same type of loss among many models, a lower loss indicates a better predictive model.
Consider the following scenario.
L is the weighted average classification loss.
n is the sample size.
For binary classification:
yj is the observed class label. The software codes it as –1 or 1, indicating the negative or positive class (or the first or second class in the
ClassNamesproperty), respectively.f(Xj) is the positive-class classification score for observation (row) j of the predictor data X.
mj = yjf(Xj) is the classification score for classifying observation j into the class corresponding to yj. Positive values of mj indicate correct classification and do not contribute much to the average loss. Negative values of mj indicate incorrect classification and contribute significantly to the average loss.
For algorithms that support multiclass classification (that is, K ≥ 3):
yj* is a vector of K – 1 zeros, with 1 in the position corresponding to the true, observed class yj. For example, if the true class of the second observation is the third class and K = 4, then y2* = [
0 0 1 0]′. The order of the classes corresponds to the order in theClassNamesproperty of the input model.f(Xj) is the length K vector of class scores for observation j of the predictor data X. The order of the scores corresponds to the order of the classes in the
ClassNamesproperty of the input model.mj = yj*′f(Xj). Therefore, mj is the scalar classification score that the model predicts for the true, observed class.
The weight for observation j is wj. The software normalizes the observation weights so that they sum to the corresponding prior class probability stored in the
Priorproperty. Therefore,
Given this scenario, the following table describes the supported loss functions that you can specify by using the LossFun name-value argument.
| Loss Function | Value of LossFun | Equation |
|---|---|---|
| Binomial deviance | "binodeviance" | |
| Observed misclassification cost | "classifcost" | where is the class label corresponding to the class with the maximal score, and is the user-specified cost of classifying an observation into class when its true class is yj. |
| Misclassified rate in decimal | "classiferror" | where I{·} is the indicator function. |
| Cross-entropy loss | "crossentropy" |
The weighted cross-entropy loss is where the weights are normalized to sum to n instead of 1. |
| Exponential loss | "exponential" | |
| Hinge loss | "hinge" | |
| Logistic loss | "logit" | |
| Minimal expected misclassification cost | "mincost" |
The software computes the weighted minimal expected classification cost using this procedure for observations j = 1,...,n.
The weighted average of the minimal expected misclassification cost loss is |
| Quadratic loss | "quadratic" |
If you use the default cost matrix (whose element value is 0 for correct classification
and 1 for incorrect classification), then the loss values for
"classifcost", "classiferror", and
"mincost" are identical. For a model with a nondefault cost matrix,
the "classifcost" loss is equivalent to the "mincost"
loss most of the time. These losses can be different if prediction into the class with
maximal posterior probability is different from prediction into the class with minimal
expected cost. Note that "mincost" is appropriate only if classification
scores are posterior probabilities.
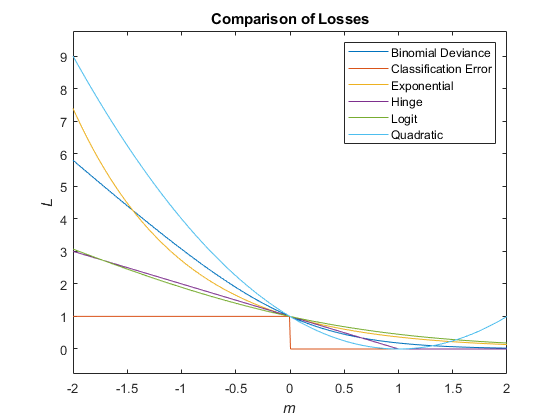
This figure compares the loss functions (except "classifcost",
"crossentropy", and "mincost") over the score
m for one observation. Some functions are normalized to pass through
the point (0,1).
Extended Capabilities
To run in parallel, set the UseParallel name-value argument to
true in the call to this function.
For more general information about parallel computing, see Run MATLAB Functions with Automatic Parallel Support (Parallel Computing Toolbox).
Version History
Introduced in R2012bIf you specify a nondefault cost matrix when you train the input model object, the oobLoss function returns a different value compared to previous releases.
The oobLoss function uses the
observation weights stored in the W property. Also, the function uses the
cost matrix stored in the Cost property if you specify the
LossFun name-value argument as "classifcost" or
"mincost". The way the function uses the W and
Cost property values has not changed. However, the property values stored in the input model object have changed for a
model with a nondefault cost matrix, so the function might return a different value.
For details about the property value change, see Cost property stores the user-specified cost matrix.
If you want the software to handle the cost matrix, prior
probabilities, and observation weights in the same way as in previous releases, adjust the prior
probabilities and observation weights for the nondefault cost matrix, as described in Adjust Prior Probabilities and Observation Weights for Misclassification Cost Matrix. Then, when you train a
classification model, specify the adjusted prior probabilities and observation weights by using
the Prior and Weights name-value arguments, respectively,
and use the default cost matrix.
See Also
loss | oobEdge | oobMargin | oobPredict | ClassificationBaggedEnsemble | fitcensemble
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)