Dynamically Change CAN IDs by CAN Pack Block Input Ports
This example shows how to dynamically control the CAN identifier (CAN ID) provided to the CAN Pack block by specifying the CAN ID through an input port.
Using this method, messages are dynamically packed with varying CAN IDs.
Explore the Model
model = 'demoDynamicCANID';
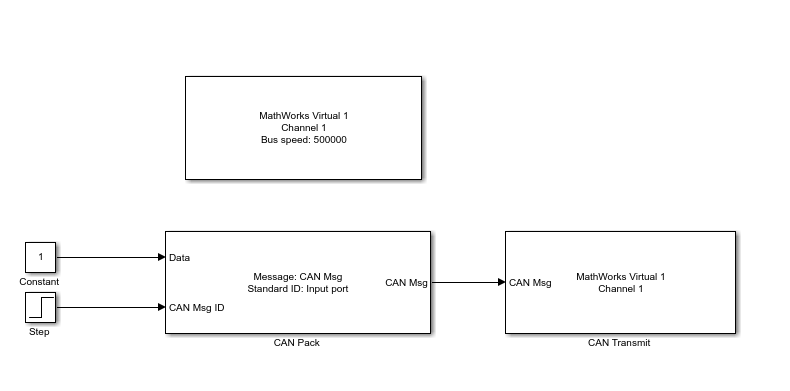
open_system(model);The model is structured to demonstrate the flow of messages from packing to transmission over a virtual CAN network. Key components include:
CAN Pack block: Configured to accept CAN IDs dynamically through an input port, facilitating the flexible packaging of CAN messages.
CAN Transmit block: Serves as the gateway for sending packed messages into the virtual CAN network.
CAN Configuration block: Configures parameters for a CAN device that you can use to transmit and receive messages.
Step block: Provides a varying input to the CAN Pack blocks.
Inspect the CAN Pack Block
Double-click the CAN Pack block to open its parameters dialog. Select the option Specify CAN identifier from input port.

Enabling this checkbox adds a new input port, allowing for the provision of changing CAN IDs dynamically.
Set Up CAN Transmit Block
The messages are packed and sent to a CAN Transmit block, which is connected to MathWorks® virtual channel 1.
Create a CAN Channel in MATLAB
To receive these messages and observe them, use MathWorks virtual channel 2.
rxCh = canChannel('MathWorks', 'Virtual 1', 2);
Start the receive channel.
start(rxCh);
Simulate the model.
sim(model);
Receive the messages in a timetable format.
rxMsg = receive(rxCh, Inf, "OutputFormat", "timetable")
rxMsg=11×8 timetable
Time ID Extended Name Data Length Signals Error Remote
__________ __ ________ __________ ___________________ ______ ____________ _____ ______
1.8717 sec 1 false {0×0 char} {[8 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]} 8 {0×0 struct} false false
2.8777 sec 1 false {0×0 char} {[8 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]} 8 {0×0 struct} false false
3.8816 sec 1 false {0×0 char} {[8 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]} 8 {0×0 struct} false false
4.8831 sec 1 false {0×0 char} {[8 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]} 8 {0×0 struct} false false
5.8903 sec 1 false {0×0 char} {[8 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]} 8 {0×0 struct} false false
6.8906 sec 5 false {0×0 char} {[8 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]} 8 {0×0 struct} false false
7.8868 sec 5 false {0×0 char} {[8 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]} 8 {0×0 struct} false false
8.8831 sec 5 false {0×0 char} {[8 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]} 8 {0×0 struct} false false
9.8793 sec 5 false {0×0 char} {[8 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]} 8 {0×0 struct} false false
10.876 sec 5 false {0×0 char} {[8 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]} 8 {0×0 struct} false false
11.874 sec 5 false {0×0 char} {[8 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]} 8 {0×0 struct} false false
Observe the change in CAN ID in the received messages.
stop(rxCh);
To visualize the varying CAN ID, plot the CAN IDs received.
plot(rxMsg.Time, rxMsg.ID); hold on data = vertcat(rxMsg.Data{:}); plot(rxMsg.Time, data(:,1)); hold off xlabel("TimeStamp"); ylabel("CAN ID Value"); legend("CAN ID","Data","Location","northeastoutside"); legend("boxoff"); yMax = max(rxMsg.ID)+5; ylim([0 yMax]);
