CSI Feedback with Autoencoders Implemented on an FPGA
This example demonstrates how to use an autoencoder neural network to compress downlink channel state information (CSI) over a clustered delay line (CDL) channel. CSI feedback is in the form of a raw channel estimate array. In this example, the autoencoder network is implemented on an FPGA using the Deep Learning HDL Toolbox™.
Introduction
In conventional 5G radio networks, CSI parameters are quantities related to the state of a channel that are extracted from the channel estimate array. The CSI feedback includes several parameters, such as the Channel Quality Indication (CQI), the precoding matrix indices (PMI) with different codebook sets, and the rank indicator (RI). The UE uses the CSI reference signal (CSI-RS) to measure and compute the CSI parameters. The user equipment (UE) reports CSI parameters to the access network node (gNB) as feedback. Upon receiving the CSI parameters, the gNB schedules downlink data transmissions with attributes such as modulation scheme, code rate, number of transmission layers, and MIMO precoding. This figure shows an overview of a CSI-RS transmission, CSI feedback, and the transmission of downlink data that is scheduled based on the CSI parameters.
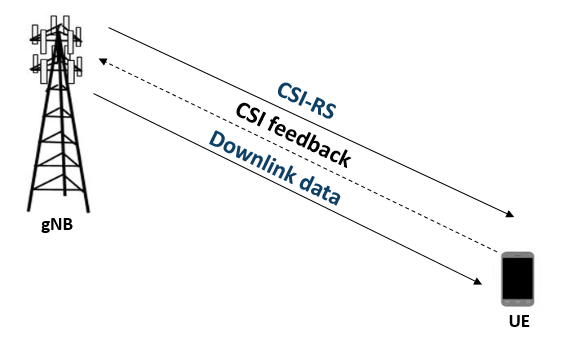
The UE processes the channel estimate to reduce the amount of CSI feedback data. As an alternative approach, the UE compresses and feeds back the channel estimate array. After receipt, the gNB decompresses and processes the channel estimate to determine downlink data link parameters. The compression and decompression can be achieved using an autoencoder neural network [1, 2]. This approach eliminates the use of existing quantized codebook and can improve overall system performance.
Define The Neural Network
This example uses a modified version of the autoencoder neural network proposed in [1].
To learn how to create the pre-trained autoencoder network, see CSI Feedback with Autoencoders (Communications Toolbox).
Load the pretrained network.
load("csiTrainedNetwork",'net','trainInfo','options','autoEncOpt'); load("predictParams.mat")
Load parameters to simulate the channel and parameters used to train the network.
maxDelay = predictParams.maxDelay; nRx = predictParams.nRx; nTx = predictParams.nTx; HTestReal = predictParams.HTestReal; numTest = predictParams.numTest;
Create and display a layerGraph for the encoder network. Replace the functionLayer in the pretrained network with a dlhdl.layer.reshapeLayer.
inputSize = [maxDelay nTx 2]; % Third dimension is real and imaginary parts nLinear = prod(inputSize); nEncoded = 64; autoencoderLGraph = layerGraph([ ... % Encoder imageInputLayer(inputSize,"Name","Htrunc", ... "Normalization","none","Name","Enc_Input") convolution2dLayer([3 3],2,"Padding","same","Name","Enc_Conv") batchNormalizationLayer("Epsilon",0.001,"MeanDecay",0.99, ... "VarianceDecay",0.99,"Name","Enc_BN") leakyReluLayer(0.3,"Name","Enc_leakyRelu") flattenLayer("Name","Enc_flatten") fullyConnectedLayer(nEncoded,"Name","Enc_FC") sigmoidLayer("Name","Enc_Sigmoid") % Decoder fullyConnectedLayer(nLinear,"Name","Dec_FC") dlhdl.layer.reshapeLayer([maxDelay nTx 2], 'Name', "Dec_Reshape") % functionLayer(@(x)dlarray(reshape(x,maxDelay,nTx,2,[]),'SSCB'), ... % "Formattable",true,"Acceleratable",true,"Name","Dec_Reshape") ]); autoencoderLGraph = ... helperCSINetAddResidualLayers(autoencoderLGraph, "Dec_Reshape"); autoencoderLGraph = addLayers(autoencoderLGraph, ... [convolution2dLayer([3 3],2,"Padding","same","Name","Dec_Conv") ... sigmoidLayer("Name","Dec_Sigmoid") ... regressionLayer("Name","Dec_Output")]); autoencoderLGraph = ... connectLayers(autoencoderLGraph,"leakyRelu_2_3","Dec_Conv"); figure plot(autoencoderLGraph) title('CSI Compression Autoencoder')

Generate A Bitstream to Run The Network
The auto encoder network includes a sigmoidLayer. To deploy the network to the FPGA hardware, you must turn on the Sigmoid property of the custom module in the deep learning processor configuration.
You can create a dlhdl.ProcessorConfig object from an existing bitstream and then modify the processor configuration properties to generate a custom bitstream. In this example, the target FPGA board is the Xilinx ZCU102 SoC board and the date type is single. hPC stores the deep learning processor configuration object created from the zcu102_single bitstream. Enable the sigmoid property of the custom module, and turn off the SegmentationBlockGeneration property to save FPGA resources.
hPC = dlhdl.ProcessorConfig('Bitstream','zcu102_single'); hPC.setModuleProperty('custom','Sigmoid','on'); hPC.setModuleProperty('conv','SegmentationBlockGeneration','off'); dlhdl.buildProcessor(hPC,ProjectFolder='mycsibitstream',ProcessorName='csibitstream');
To learn how to use the generated bitstream file, see Generate Custom Bitstream.
Define FPGA Board Interface
Define the target FPGA board programming interface by using the dlhdl.Target object. Specify that the interface is for a Xilinx® board with an Ethernet interface.
hTarget = dlhdl.Target('Xilinx','Interface','Ethernet');
To use the JTAG interface, install Xilinx™ Vivado™ Design Suite 2023.1. To set the Xilinx Vivado toolpath, enter:
hdlsetuptoolpath('ToolName', 'Xilinx Vivado', 'ToolPath', 'C:\Xilinx\Vivado\2023.1\bin\vivado.bat'); hTarget = dlhdl.Target('Xilinx','Interface','JTAG');
Prepare The Network for Deployment
Prepare the network for deployment by creating a dlhdl.Workflow object. Specify the network and the bitstream name. Ensure that the bitstream name matches the data type and the FPGA board. In this example the target FPGA board is the Xilinx ZCU102 SOC board. The bitstream uses a single data type. Set bistreamPath to the path of the MAT file and .bit file generated by the dlhdl.buildProcessor function. See Generate Custom Bitstream.
bitStreamPath = fullfile('mycsibitstream','csibitstream.bit')
bitStreamPath = 'mycsibitstream\csibitstream.bit'
hW = dlhdl.Workflow(Network=net,Bitstream=bitStreamPath,Target=hTarget);
To run the example on a Xilinx ZC706 board, enter:
hW = dlhdl.Workflow('Network', snet, 'Bitstream', 'zc706_lstm_single','Target',hTarget);
compile(hW,'InputFrameNumberLimit',numTest);### Compiling network for Deep Learning FPGA prototyping ...
### Targeting FPGA bitstream mycsibitstream\csibitstream.bit.
### Optimizing network: Layer ('Enc_flatten'), removed. "nnet.cnn.layer.FlattenLayer" layers can be omitted from networks if they are followed by a fullyConnectedLayer.
### Optimizing network: Fused 'nnet.cnn.layer.BatchNormalizationLayer' into 'nnet.cnn.layer.Convolution2DLayer'
### Optimizing network: Reshape layer ('Dec_Reshape'), removed and fused into FC layer ('Dec_FC'). The weights of the FC layer were modified to account for the reshape layer removal.
### The network includes the following layers:
1 'Enc_Input' Image Input 28×8×2 images (SW Layer)
2 'Enc_Conv' 2-D Convolution 2 3×3×2 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding 'same' (HW Layer)
3 'Enc_leakyRelu' Leaky ReLU Leaky ReLU with scale 0.3 (HW Layer)
4 'Enc_FC' Fully Connected 64 fully connected layer (HW Layer)
5 'Enc_Sigmoid' Sigmoid sigmoid (HW Layer)
6 'Dec_FC' Fully Connected 896 fully connected layer (HW Layer)
7 'Dec_Reshape' Reshape Layer reshapeLayer [28 8 2] (HW Layer)
8 'Res_Conv_1_1' 2-D Convolution 8 3×3×2 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding 'same' (HW Layer)
9 'leakyRelu_1_1' Leaky ReLU Leaky ReLU with scale 0.3 (HW Layer)
10 'Res_Conv_1_2' 2-D Convolution 16 3×3×8 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding 'same' (HW Layer)
11 'leakyRelu_1_2' Leaky ReLU Leaky ReLU with scale 0.3 (HW Layer)
12 'Res_Conv_1_3' 2-D Convolution 2 3×3×16 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding 'same' (HW Layer)
13 'add_1' Addition Element-wise addition of 2 inputs (HW Layer)
14 'leakyRelu_1_3' Leaky ReLU Leaky ReLU with scale 0.3 (HW Layer)
15 'Res_Conv_2_1' 2-D Convolution 8 3×3×2 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding 'same' (HW Layer)
16 'leakyRelu_2_1' Leaky ReLU Leaky ReLU with scale 0.3 (HW Layer)
17 'Res_Conv_2_2' 2-D Convolution 16 3×3×8 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding 'same' (HW Layer)
18 'leakyRelu_2_2' Leaky ReLU Leaky ReLU with scale 0.3 (HW Layer)
19 'Res_Conv_2_3' 2-D Convolution 2 3×3×16 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding 'same' (HW Layer)
20 'add_2' Addition Element-wise addition of 2 inputs (HW Layer)
21 'leakyRelu_2_3' Leaky ReLU Leaky ReLU with scale 0.3 (HW Layer)
22 'Dec_Conv' 2-D Convolution 2 3×3×2 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding 'same' (HW Layer)
23 'Dec_Sigmoid' Sigmoid sigmoid (HW Layer)
24 'Dec_Output' Regression Output mean-squared-error (SW Layer)
### Notice: The layer 'Enc_Input' with type 'nnet.cnn.layer.ImageInputLayer' is implemented in software.
### Notice: The layer 'Dec_Output' with type 'nnet.cnn.layer.RegressionOutputLayer' is implemented in software.
### Compiling layer group: Enc_Conv>>Enc_leakyRelu ...
### Compiling layer group: Enc_Conv>>Enc_leakyRelu ... complete.
### Compiling layer group: Enc_FC ...
### Compiling layer group: Enc_FC ... complete.
### Compiling layer group: Dec_FC ...
### Compiling layer group: Dec_FC ... complete.
### Compiling layer group: Res_Conv_1_1>>Res_Conv_1_3 ...
### Compiling layer group: Res_Conv_1_1>>Res_Conv_1_3 ... complete.
### Compiling layer group: Res_Conv_2_1>>Res_Conv_2_3 ...
### Compiling layer group: Res_Conv_2_1>>Res_Conv_2_3 ... complete.
### Compiling layer group: Dec_Conv ...
### Compiling layer group: Dec_Conv ... complete.
### Allocating external memory buffers:
offset_name offset_address allocated_space
_______________________ ______________ ________________
"InputDataOffset" "0x00000000" "6.8 MB"
"OutputResultOffset" "0x006d6000" "6.8 MB"
"SchedulerDataOffset" "0x00dac000" "468.0 kB"
"SystemBufferOffset" "0x00e21000" "52.0 kB"
"InstructionDataOffset" "0x00e2e000" "56.0 kB"
"ConvWeightDataOffset" "0x00e3c000" "20.0 kB"
"FCWeightDataOffset" "0x00e41000" "452.0 kB"
"EndOffset" "0x00eb2000" "Total: 14.7 MB"
### Network compilation complete.
deploy(hW);
### Programming FPGA Bitstream using Ethernet...
### Attempting to connect to the hardware board at 172.21.59.90...
### Connection successful
### Programming FPGA device on Xilinx SoC hardware board at 172.21.59.90...
### Attempting to connect to the hardware board at 172.21.59.90...
### Connection successful
### Copying FPGA programming files to SD card...
### Setting FPGA bitstream and devicetree for boot...
# Copying Bitstream csibitstream.bit to /mnt/hdlcoder_rd
# Set Bitstream to hdlcoder_rd/csibitstream.bit
# Copying Devicetree devicetree_dlhdl.dtb to /mnt/hdlcoder_rd
# Set Devicetree to hdlcoder_rd/devicetree_dlhdl.dtb
# Set up boot for Reference Design: 'AXI-Stream DDR Memory Access : 3-AXIM'
### Programming done. The system will now reboot for persistent changes to take effect.
### Rebooting Xilinx SoC at 172.21.59.90...
### Reboot may take several seconds...
### Attempting to connect to the hardware board at 172.21.59.90...
### Connection successful
### Programming the FPGA bitstream has been completed successfully.
### Loading weights to Conv Processor.
### Conv Weights loaded. Current time is 11-Jul-2024 21:59:26
### Loading weights to FC Processor.
### 50% finished, current time is 11-Jul-2024 21:59:26.
### FC Weights loaded. Current time is 11-Jul-2024 21:59:26
Testing The FPGA Implementation
Get the deployed network activations by using the predict method of the dlhdl.Workflow object. Use the predict function to retrieve the Deep Learning Toolbox™ predictions and compare them both.
HTestRealHat = predict(net,HTestReal); HTestRealHatFPGA = predict(hW,HTestReal);
### Finished writing input activations. ### Running in multi-frame mode with 2000 inputs.
The deltaMax value is the comparison between the accuracy of predictions from the Deep Learning Toolbox™ (HTestRealHat) and prediction results from the FPGA (HTestRealHatFPGA). The FPGA predictions are very close to the ground truth predictions from the Deep Learning Toolbox.
deltaMax = max(abs(HTestRealHat - HTestRealHatFPGA),[],'all')deltaMax = single
3.4571e-06
References
[1] Wen, Chao-Kai, Wan-Ting Shih, and Shi Jin. “Deep Learning for Massive MIMO CSI Feedback.” IEEE Wireless Communications Letters 7, no. 5 (October 2018): 748–51. https://doi.org/10.1109/LWC.2018.2818160.
[2] Zimaglia, Elisa, Daniel G. Riviello, Roberto Garello, and Roberto Fantini. “A Novel Deep Learning Approach to CSI Feedback Reporting for NR 5G Cellular Systems.” In 2020 IEEE Microwave Theory and Techniques in Wireless Communications (MTTW), 47–52. Riga, Latvia: IEEE, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/MTTW51045.2020.9245055.
See Also
dlhdl.Workflow | compile | deploy | predict | dlhdl.ProcessorConfig | dlhdl.buildProcessor
Topics
- CSI Feedback with Autoencoders (Communications Toolbox)
- Generate Custom Bitstream