step
System object: phased.RectangularWaveform
Namespace: phased
Samples of rectangular pulse waveform
Syntax
Y = step(sRFM)
Y = step(sRFM,prfidx)
Y = step(sRFM,freqoffset)
[Y,PRF] = step(___)
[Y,COEFF] = step(___)
Description
Note
Starting in R2016b, instead of using the step method
to perform the operation defined by the System object™, you can
call the object with arguments, as if it were a function. For example, y
= step(obj,x) and y = obj(x) perform
equivalent operations. When the only argument to the step method
is the System object itself, replace y = step(obj) by y
= obj().
Y = step(sRFM) returns samples of a rectangular
pulse in the column vector Y.
Y = step(sRFM,prfidx), uses the prfidx index to
select the PRF from the predefined vector of values specified by the
PRF property. This syntax applies when you set the
PRFSelectionInputPort property to
true.
Y = step(sRFM,freqoffset), uses the
freqoffset to generate the waveform with an offset as specified
at step time. Use this syntax for cases where the transmit pulse frequency needs to be
dynamically updated. This syntax applies when you set the
FrequencyOffsetSource property to 'Input
port'.
[Y,PRF] = step(___) also returns the current pulse
repetition frequency, PRF. To enable this syntax, set the
PRFOutputPort property to true and set the
OutputFormat property to 'Pulses'.
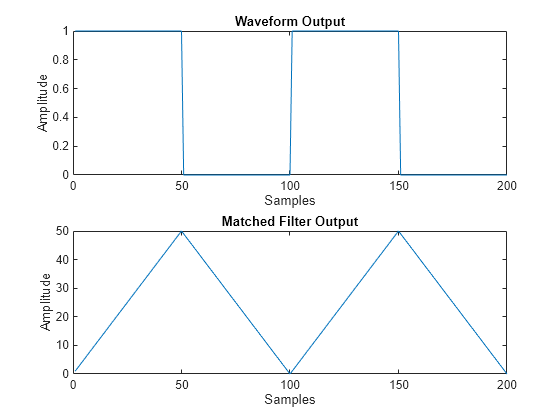
[Y,COEFF] = step(___) returns the matched filter
coefficients, COEFF, for the current pulse. To enable this syntax,
set CoefficientsOutputPort to true.
COEFF is returned as either an
NZ-by-1 vector or an
NZ-by-M matrix.
An NZ-by-1 vector is returned when:
The object has
OutputFormatset to'Pulses'andNumPulsesis equal to 1. NZ is the pulse width.The object is configured to generate constant pulse width waveforms (
DurationSpecificationis set to'Pulse width'or'Duty cycle'andPRFhas one unique value); and eitherOutputFormatis set to'Pulses'andNumPulsesis greater than 1, orOutputFormatis set to'Samples'. For this case, NZ is the pulse width.
An NZ-by-M matrix is returned when the object generates varying pulse widths (
DurationSpecificationis set to'Duty cycle'andPRFhas more than one unique value); and eitherOutputFormatset to'Pulses'andNumPulsesis greater than 1, orOutputFormatis set to'Samples'. For this case, NZ is the pulse width, and M is the number of sub-pulses,NumSteps.
You can combine optional input and output arguments when their enabling properties are
set. Optional inputs and outputs must be listed in the same order as the order of the
enabling properties. For example, [Y,PRF,COEFF] =
step(sRFM,prfidx,freqoffset).
Note
The object performs an initialization the first time the object is executed. This
initialization locks nontunable properties
and input specifications, such as dimensions, complexity, and data type of the input data.
If you change a nontunable property or an input specification, the System object issues an error. To change nontunable properties or inputs, you must first
call the release method to unlock the object.