Rotational Spring
Ideal spring in mechanical rotational systems
Libraries:
Simscape /
Foundation Library /
Mechanical /
Rotational Elements
Description
The Rotational Spring block represents an ideal mechanical rotational linear spring, described with the following equations:
where
T is torque transmitted through the spring.
K is spring rate.
φ is relative displacement angle, that is, spring deformation.
φinit is spring preliminary winding.
φR and φC are absolute angular displacements of ports R and C, respectively.
ω is relative angular velocity.
t is time.
The block positive direction is from port R to port C. This means that if the port R velocity is greater than that of port C, the block transmits torque from R to C.
Variables
To set the priority and initial target values for the block variables prior to simulation, use the Initial Targets section in the block dialog box or Property Inspector. For more information, see Set Priority and Initial Target for Block Variables.
Nominal values provide a way to specify the expected magnitude of a variable in a model. Using system scaling based on nominal values increases the simulation robustness. Nominal values can come from different sources, one of which is the Nominal Values section in the block dialog box or Property Inspector. For more information, see Modify Nominal Values for a Block Variable.
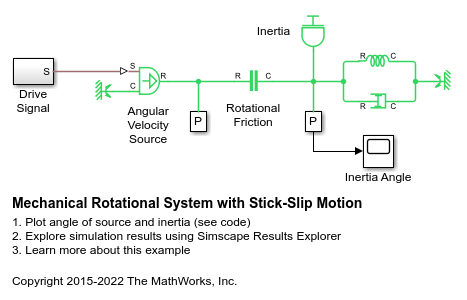
Examples
Ports
Conserving
Parameters
Extended Capabilities
Version History
Introduced in R2007a
See Also
Rotational Damper | Rotational Friction | Rotational Hard Stop