laguerreL
Generalized Laguerre Function and Laguerre Polynomials
Description
laguerreL(
returns the Laguerre polynomial of degree n,x)n if
n is a nonnegative integer. When n is
not a nonnegative integer, laguerreL returns the Laguerre
function. For details, see Generalized Laguerre Function.
Examples
Find Laguerre Polynomials for Numeric and Symbolic Inputs
Find the Laguerre polynomial of degree 3
for input 4.3.
laguerreL(3,4.3)
ans =
2.5838Find the Laguerre polynomial for symbolic inputs. Specify degree
n as 3 to return the explicit form of
the polynomial.
syms x laguerreL(3,x)
ans = - x^3/6 + (3*x^2)/2 - 3*x + 1
If the degree of the Laguerre polynomial n is not specified,
laguerreL cannot find the polynomial. When
laguerreL cannot find the polynomial, it returns the
function call.
syms n x laguerreL(n,x)
ans = laguerreL(n, x)
Find Generalized Laguerre Polynomial
Find the explicit form of the generalized Laguerre polynomial
L(n,a,x) of degree n = 2.
syms a x laguerreL(2,a,x)
ans = (3*a)/2 - x*(a + 2) + a^2/2 + x^2/2 + 1
Return Generalized Laguerre Function
When n is not a nonnegative integer,
laguerreL(n,a,x) returns the generalized Laguerre
function.
laguerreL(-2.7,3,2)
ans =
0.2488laguerreL is not defined for certain inputs and returns an
error.
syms x
laguerreL(-5/2, -3/2, x)Error using symengine Function 'laguerreL' not supported for parameter values '-5/2' and '-3/2'.
Find Laguerre Polynomial with Vector and Matrix Inputs
Find the Laguerre polynomials of degrees 1
and 2 by setting n = [1 2].
syms x laguerreL([1 2],x)
ans = [ 1 - x, x^2/2 - 2*x + 1]
laguerreL acts element-wise on n to return
a vector with two elements.
If multiple inputs are specified as a vector, matrix, or multidimensional array,
the inputs must be the same size. Find the generalized Laguerre polynomials where
input arguments n and x are
matrices.
syms a n = [2 3; 1 2]; xM = [x^2 11/7; -3.2 -x]; laguerreL(n,a,xM)
ans =
[ a^2/2 - a*x^2 + (3*a)/2 + x^4/2 - 2*x^2 + 1,...
a^3/6 + (3*a^2)/14 - (253*a)/294 - 676/1029]
[ a + 21/5,...
a^2/2 + a*x + (3*a)/2 + x^2/2 + 2*x + 1]laguerreL acts element-wise on n and
x to return a matrix of the same size as n
and x.
Differentiate and Find Limits of Laguerre Polynomials
Use limit to find the limit of a
generalized Laguerre polynomial of degree 3 as
x tends to ∞.
syms x expr = laguerreL(3,2,x); limit(expr,x,Inf)
ans = -Inf
Use diff to find the third derivative of the generalized
Laguerre polynomial laguerreL(n,a,x).
syms n a expr = laguerreL(n,a,x); diff(expr,x,3)
ans = -laguerreL(n - 3, a + 3, x)
Find Taylor Series Expansion of Laguerre Polynomials
Use taylor to find the Taylor series
expansion of the generalized Laguerre polynomial of degree 2
at x = 0.
syms a x expr = laguerreL(2,a,x); taylor(expr,x)
ans = (3*a)/2 - x*(a + 2) + a^2/2 + x^2/2 + 1
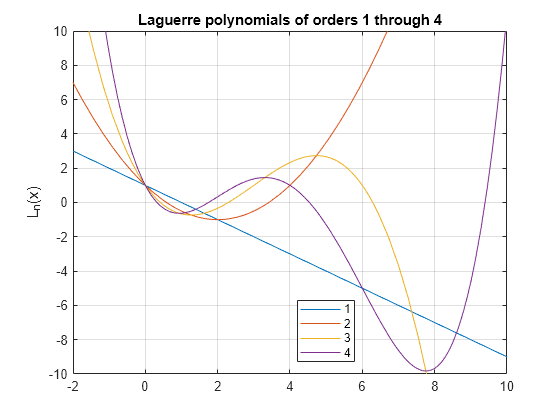
Plot Laguerre Polynomials
Plot the Laguerre polynomials of orders 1 through 4.
syms x fplot(laguerreL(1:4,x)) axis([-2 10 -10 10]) grid on ylabel('L_n(x)') title('Laguerre polynomials of orders 1 through 4') legend('1','2','3','4','Location','best')
Input Arguments
More About
Algorithms
The generalized Laguerre function is not defined for all values of parameters
nandabecause certain restrictions on the parameters exist in the definition of the hypergeometric functions. If the generalized Laguerre function is not defined for a particular pair ofnanda, thelaguerreLfunction returns an error message. See Return Generalized Laguerre Function.The calls
laguerreL(n,x)andlaguerreL(n,0,x)are equivalent.If
nis a nonnegative integer, thelaguerreLfunction returns the explicit form of the corresponding Laguerre polynomial.The special values are implemented for arbitrary values of
nanda.If
nis a negative integer andais a numerical noninteger value satisfying a ≥ -n, thenlaguerreLreturns0.If
nis a negative integer andais an integer satisfying a < -n, the function returns an explicit expression defined by the reflection ruleIf all arguments are numerical and at least one argument is a floating-point number, then
laguerreL(x)returns a floating-point number. For all other arguments,laguerreL(n,a,x)returns a symbolic function call.
Version History
Introduced in R2014b
See Also
chebyshevT | chebyshevU | gegenbauerC | hermiteH | hypergeom | jacobiP | legendreP