FunctionContour Properties
Function contour chart appearance and behavior
FunctionContour properties control
the appearance and behavior of FunctionContour objects. By changing property values, you
can modify certain aspects of the chart.
Levels
Contour levels, specified as a vector of z values. By default,
the fcontour function chooses values that span
the range of values in the ZData property.
Setting this property sets the associated mode property to manual.
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64
Selection mode for the LevelList, specified
as one of these values:
'auto'— Determine the values based on theZDatavalues.'manual'— Use manually specified values. To specify the values, set theLevelListproperty. When the mode is'manual', theLevelListvalues do not change if you change theFunctionproperty or the limits.
Spacing between contour lines, specified as a scalar numeric
value. For example, specify a value of 2 to draw
contour lines at increments of 2. By default, LevelStep is
determined by using the ZData values.
Setting this property sets the associated mode property to 'manual'.
Example: 3.4
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64
Selection mode for the LevelStep, specified
as one of these values:
'auto'— Determine the value based on theZDatavalues.'manual'— Use a manually specified value. To specify the value, set theLevelStepproperty. When the mode is'manual', the value ofLevelStepModedoes not change when theFunctionproperty or the limits change.
Color and Styling
Fill between contour lines, specified as 'on' or 'off',
or as numeric or logical 1 (true) or
0 (false). A value of 'on'
is equivalent to true, and 'off' is equivalent to
false. Thus, you can use the value of this property as a logical
value. The value is stored as an on/off logical value of type matlab.lang.OnOffSwitchState.
A value of
'on'fill the spaces between contour lines with color.A value of
'off'leaves the spaces between the contour lines unfilled.
Color of contour lines, specified as 'flat', an RGB triplet, a
hexadecimal color code, a color name, or a short name. To use a different color for each
contour line, specify 'flat'. The color is determined by the contour
value of the line, the colormap, and the scaling of data values into the colormap. For
more information on color scaling, see Control Colormap Limits.
To use the same color for all the contour lines, specify an RGB triplet, a hexadecimal color code, a color name, or a short name.
For a custom color, specify an RGB triplet or a hexadecimal color code.
An RGB triplet is a three-element row vector whose elements specify the intensities of the red, green, and blue components of the color. The intensities must be in the range
[0,1], for example,[0.4 0.6 0.7].A hexadecimal color code is a string scalar or character vector that starts with a hash symbol (
#) followed by three or six hexadecimal digits, which can range from0toF. The values are not case sensitive. Therefore, the color codes"#FF8800","#ff8800","#F80", and"#f80"are equivalent.
Alternatively, you can specify some common colors by name. This table lists the named color options, the equivalent RGB triplets, and the hexadecimal color codes.
| Color Name | Short Name | RGB Triplet | Hexadecimal Color Code | Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
"red" | "r" | [1 0 0] | "#FF0000" |
|
"green" | "g" | [0 1 0] | "#00FF00" |
|
"blue" | "b" | [0 0 1] | "#0000FF" |
|
"cyan"
| "c" | [0 1 1] | "#00FFFF" |
|
"magenta" | "m" | [1 0 1] | "#FF00FF" |
|
"yellow" | "y" | [1 1 0] | "#FFFF00" |
|
"black" | "k" | [0 0 0] | "#000000" |
|
"white" | "w" | [1 1 1] | "#FFFFFF" |
|
"none" | Not applicable | Not applicable | Not applicable | No color |
This table lists the default color palettes for plots in the light and dark themes.
| Palette | Palette Colors |
|---|---|
Before R2025a: Most plots use these colors by default. |
|
|
|
You can get the RGB triplets and hexadecimal color codes for these palettes using the orderedcolors and rgb2hex functions. For example, get the RGB triplets for the "gem" palette and convert them to hexadecimal color codes.
RGB = orderedcolors("gem");
H = rgb2hex(RGB);Before R2023b: Get the RGB triplets using RGB =
get(groot,"FactoryAxesColorOrder").
Before R2024a: Get the hexadecimal color codes using H =
compose("#%02X%02X%02X",round(RGB*255)).
Line style, specified as one of the options listed in this table.
| Line Style | Description | Resulting Line |
|---|---|---|
"-" | Solid line |
|
"--" | Dashed line |
|
":" | Dotted line |
|
"-." | Dash-dotted line |
|
"none" | No line | No line |
Line width, specified as a positive value in points, where 1 point = 1/72 of an inch. If the line has markers, then the line width also affects the marker edges.
The line width cannot be thinner than the width of a pixel. If you set the line width to a value that is less than the width of a pixel on your system, the line displays as one pixel wide.
Function
Function to plot, specified as a function handle, anonymous function, or a symbolic expression or function.
Plotting interval for x values, specified
as a two-element vector of the form [xmin xmax].
Selection mode for XRange, specified as one
of these values:
'auto'— Use the default value[-5 5]. If axes limits are specified, follow the specified limits instead.'manual'— Use manually specified values. To specify the values, set theXRangeproperty.
Plotting interval for y values, specified
as a two-element vector of the form [ymin ymax].
Selection mode for YRange, specified as one
of these values:
'auto'— Use the default value[-5 5]. If the axes limits are specified, follow the specified limits instead.'manual'— Use manually specified values. To specify the values, set theYRangeproperty.
Number of evaluation points per direction, specified as a number.
The default is 71. Because fcontour uses
adaptive evaluation, the actual number of evaluation points is greater.
Example: 30
Data
This property is read-only.
Contour matrix, returned as a two-row matrix of following form.
Z1, x1,1, x1,2, ..., x1,N1, Z2, x2,1, x2,2, ..., x2,N2, Z3, ... N1, y1,1, y1,2, ..., y1,N1, N2, y2,1, y2,2, ..., y2,N2, N3, ...
The columns of the matrix define the contour lines. Each contour line starts with a column containing Z and N values:
Zi — The height of the ith contour line
Ni — The number of vertices in the ith contour line
(xij, yij) — The coordinates of the vertices for the ith contour line, where j ranges from 1 to Ni
Example
Create a contour plot of x^2 +
y^2. For demonstration purposes, use the
lowest MeshDensity that results
in a plot, which is 3.
h = fcontour(@(x,y) x.^2+y.^2, 'MeshDensity', 3); grid on
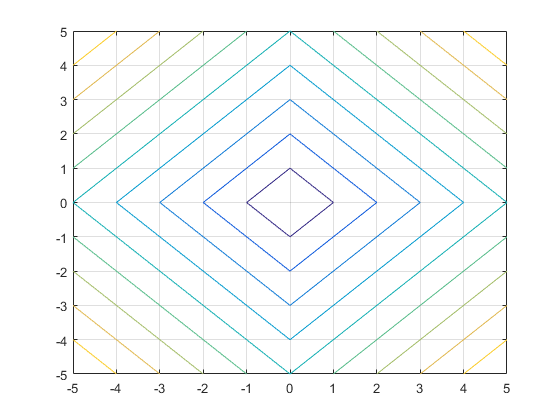
Get the contour matrix using the
ContourMatrix property of the
contour object
(h.ContourMatrix). The contour
matrix contains definitions for each of the
contour lines. Here are the first 12 columns of
the matrix.
h.ContourMatrix
ans = Columns 1 through 23 5 1 0 -1 0 1 10 2 0 -2 0 2 ... 5 0 -1 0 1 0 5 0 -2 0 2 0 ...
The first definition in the matrix indicates
that there is a contour line drawn at level
5, consisting of the five
vertices (1, 0), (0,
-1), (-1, 0),
(0, 1), and (1,
0). The second definition indicates that
there is a contour line at level
10, consisting of the five
vertices (2, 0), (0,
-2), (-2, 0),
(0, 2), and (2,
0).
This property is read-only.
x values specified as a matrix. XData is
at least a 2-by-2 matrix. size(XData), size(YData),
and size(ZData) are equal.
This property is read-only.
y values, specified as a matrix. YData is
at least a 2-by-2 matrix. size(XData), size(YData),
and size(ZData) are equal.
This property is read-only.
Data that defines the surface to contour, specified as a matrix. ZData is
at least a 2-by-2 matrix. size(XData), size(YData),
and size(ZData) are equal.
Legend
Text for legend label, specified as a custom character vector or string. The default label is
autogenerated from the Function property and the
texlabel function. The legend does not appear until you call
the legend function.
Data Types: char | string
Include the object in the legend, specified as an Annotation
object. Set the underlying IconDisplayStyle property of the
Annotation object to one of these values:
"on"— Include the object in the legend (default)."off"— Do not include the object in the legend.
For example, to exclude the FunctionContour object named
obj from the legend, set the IconDisplayStyle
property to "off".
obj.Annotation.LegendInformation.IconDisplayStyle = "off";
Alternatively, you can control the items in a legend using the legend function. Specify the first input argument as a vector of the
graphics objects to include. If you do not specify an existing graphics object in the
first input argument, then it does not appear in the legend. However, graphics objects
added to the axes after the legend is created do appear in the legend. Consider creating
the legend after creating all the plots to avoid extra items.
Interactivity
State of visibility, specified as "on" or "off", or as
numeric or logical 1 (true) or
0 (false). A value of "on"
is equivalent to true, and "off" is equivalent to
false. Thus, you can use the value of this property as a logical
value. The value is stored as an on/off logical value of type matlab.lang.OnOffSwitchState.
"on"— Display the object."off"— Hide the object without deleting it. You still can access the properties of an invisible object.
Data tip content, specified as a DataTipTemplate object. You can
control the content that appears in a data tip by modifying the properties of the
underlying DataTipTemplate object. For a list of properties, see
DataTipTemplate Properties.
For an example of modifying data tips, see Create Custom Data Tips.
Note
The DataTipTemplate object is not returned by
findobj or findall, and it is not
copied by copyobj.
Context menu, specified as a ContextMenu object. Use this property
to display a context menu when you right-click the object. Create the context menu using
the uicontextmenu function.
Note
If the PickableParts property is set to
'none' or if the HitTest property is set
to 'off', then the context menu does not appear.
Selection state, specified as 'on' or 'off', or as
numeric or logical 1 (true) or
0 (false). A value of 'on'
is equivalent to true, and 'off' is equivalent to
false. Thus, you can use the value of this property as a logical
value. The value is stored as an on/off logical value of type matlab.lang.OnOffSwitchState.
'on'— Selected. If you click the object when in plot edit mode, then MATLAB® sets itsSelectedproperty to'on'. If theSelectionHighlightproperty also is set to'on', then MATLAB displays selection handles around the object.'off'— Not selected.
Display of selection handles when selected, specified as 'on' or
'off', or as numeric or logical 1
(true) or 0 (false). A
value of 'on' is equivalent to true, and
'off' is equivalent to false. Thus, you can
use the value of this property as a logical value. The value is stored as an on/off
logical value of type matlab.lang.OnOffSwitchState.
'on'— Display selection handles when theSelectedproperty is set to'on'.'off'— Never display selection handles, even when theSelectedproperty is set to'on'.
Callbacks
Mouse-click callback, specified as one of these values:
Function handle
Cell array containing a function handle and additional arguments
Character vector that is a valid MATLAB command or function, which is evaluated in the base workspace (not recommended)
Use this property to execute code when you click the object. If you specify this property using a function handle, then MATLAB passes two arguments to the callback function when executing the callback:
Clicked object — Access properties of the clicked object from within the callback function.
Event data — Empty argument. Replace it with the tilde character (
~) in the function definition to indicate that this argument is not used.
For more information on how to use function handles to define callback functions, see Create Callbacks for Graphics Objects.
Note
If the PickableParts property is set to 'none' or
if the HitTest property is set to 'off',
then this callback does not execute.
Object creation function, specified as one of these values:
Function handle.
Cell array in which the first element is a function handle. Subsequent elements in the cell array are the arguments to pass to the callback function.
Character vector containing a valid MATLAB expression (not recommended). MATLAB evaluates this expression in the base workspace.
For more information about specifying a callback as a function handle, cell array, or character vector, see Create Callbacks for Graphics Objects.
This property specifies a callback function to execute when MATLAB creates the object. MATLAB initializes all property values before executing the CreateFcn callback. If you do not specify the CreateFcn property, then MATLAB executes a default creation function.
Setting the CreateFcn property on an existing component has no effect.
If you specify this property as a function handle or cell array, you can access the object that is being created using the first argument of the callback function. Otherwise, use the gcbo function to access the object.
Object deletion function, specified as one of these values:
Function handle.
Cell array in which the first element is a function handle. Subsequent elements in the cell array are the arguments to pass to the callback function.
Character vector containing a valid MATLAB expression (not recommended). MATLAB evaluates this expression in the base workspace.
For more information about specifying a callback as a function handle, cell array, or character vector, see Create Callbacks for Graphics Objects.
This property specifies a callback function to execute when MATLAB deletes the object. MATLAB executes the DeleteFcn callback before destroying the
properties of the object. If you do not specify the DeleteFcn
property, then MATLAB executes a default deletion function.
If you specify this property as a function handle or cell array, you can access the object that is being deleted using the first argument of the callback function. Otherwise, use the gcbo function to access the object.
Callback Execution Control
Callback interruption, specified as 'on' or 'off', or as
numeric or logical 1 (true) or
0 (false). A value of 'on'
is equivalent to true, and 'off' is equivalent to
false. Thus, you can use the value of this property as a logical
value. The value is stored as an on/off logical value of type matlab.lang.OnOffSwitchState.
This property determines if a running callback can be interrupted. There are two callback states to consider:
The running callback is the currently executing callback.
The interrupting callback is a callback that tries to interrupt the running callback.
MATLAB determines callback interruption behavior whenever it executes a command that
processes the callback queue. These commands include drawnow, figure, uifigure, getframe, waitfor, and pause.
If the running callback does not contain one of these commands, then no interruption occurs. MATLAB first finishes executing the running callback, and later executes the interrupting callback.
If the running callback does contain one of these commands, then the
Interruptible property of the object that owns the running
callback determines if the interruption occurs:
If the value of
Interruptibleis'off', then no interruption occurs. Instead, theBusyActionproperty of the object that owns the interrupting callback determines if the interrupting callback is discarded or added to the callback queue.If the value of
Interruptibleis'on', then the interruption occurs. The next time MATLAB processes the callback queue, it stops the execution of the running callback and executes the interrupting callback. After the interrupting callback completes, MATLAB then resumes executing the running callback.
Note
Callback interruption and execution behave differently in these situations:
If the interrupting callback is a
DeleteFcn,CloseRequestFcn, orSizeChangedFcncallback, then the interruption occurs regardless of theInterruptibleproperty value.If the running callback is currently executing the
waitforfunction, then the interruption occurs regardless of theInterruptibleproperty value.If the interrupting callback is owned by a
Timerobject, then the callback executes according to schedule regardless of theInterruptibleproperty value.
Callback queuing, specified as 'queue' or 'cancel'. The BusyAction property determines how MATLAB handles the execution of interrupting callbacks. There are two callback states to consider:
The running callback is the currently executing callback.
The interrupting callback is a callback that tries to interrupt the running callback.
The BusyAction property determines callback queuing behavior only
when both of these conditions are met:
Under these conditions, the BusyAction property of the
object that owns the interrupting callback determines how MATLAB handles the interrupting callback. These are possible values of the
BusyAction property:
'queue'— Puts the interrupting callback in a queue to be processed after the running callback finishes execution.'cancel'— Does not execute the interrupting callback.
Ability to capture mouse clicks, specified as one of these values:
'visible'— Capture mouse clicks only when visible. TheVisibleproperty must be set to'on'. TheHitTestproperty determines if theFunctionContourobject responds to the click or if an ancestor does.'none'— Cannot capture mouse clicks. Clicking theFunctionContourobject passes the click to the object behind it in the current view of the figure window. TheHitTestproperty of theFunctionContourobject has no effect.
Response to captured mouse clicks, specified as 'on' or
'off', or as numeric or logical 1
(true) or 0 (false). A
value of 'on' is equivalent to true, and 'off' is
equivalent to false. Thus, you can use the value of this property as
a logical value. The value is stored as an on/off logical value of type matlab.lang.OnOffSwitchState.
'on'— Trigger theButtonDownFcncallback of theFunctionContourobject. If you have defined theContextMenuproperty, then invoke the context menu.'off'— Trigger the callbacks for the nearest ancestor of theFunctionContourobject that meets one of these conditions:HitTestproperty is set to'on'.PickablePartsproperty is set to a value that enables the ancestor to capture mouse clicks.
Note
The PickableParts property determines if
the FunctionContour object can capture
mouse clicks. If it cannot, then the HitTest property
has no effect.
This property is read-only.
Deletion status, returned as an on/off logical value of type matlab.lang.OnOffSwitchState.
MATLAB sets the BeingDeleted property to
'on' when the DeleteFcn callback begins
execution. The BeingDeleted property remains set to
'on' until the component object no longer exists.
Check the value of the BeingDeleted property to verify that the object is not about to be deleted before querying or modifying it.
Parent/Child
Parent, specified as an Axes, Group,
or Transform object.
Children, returned as an empty GraphicsPlaceholder array or a
DataTip object array. Use this property to view a list of data tips
that are plotted on the chart.
You cannot add or remove children using the Children property. To add a
child to this list, set the Parent property of the
DataTip object to the chart object.
Visibility of the object handle in the Children property
of the parent, specified as one of these values:
"on"— Object handle is always visible."off"— Object handle is invisible at all times. This option is useful for preventing unintended changes by another function. SetHandleVisibilityto"off"to temporarily hide the handle during the execution of that function."callback"— Object handle is visible from within callbacks or functions invoked by callbacks, but not from within functions invoked from the command line. This option blocks access to the object at the command line, but permits callback functions to access it.
If the object is not listed in the Children property of the parent, then
functions that obtain object handles by searching the object hierarchy or querying
handle properties cannot return it. Examples of such functions include the
get, findobj, gca, gcf, gco, newplot, cla, clf, and close functions.
Hidden object handles are still valid. Set the root ShowHiddenHandles
property to "on" to list all object handles regardless of their
HandleVisibility property setting.
Identifiers
This property is read-only.
Type of graphics object, returned as
'functioncontour'. Use this
property to find all objects of a given type within
a plotting hierarchy, for example, searching for the
type using findobj.
Object identifier, specified as a character vector or string scalar. You can specify a unique Tag value to serve as an identifier for an object. When you need access to the object elsewhere in your code, you can use the findobj function to search for the object based on the Tag value.
User data, specified as any MATLAB array. For example, you can specify a scalar, vector, matrix, cell array, character array, table, or structure. Use this property to store arbitrary data on an object.
If you are working in App Designer, create public or private properties in the app to share data instead of using the UserData property. For more information, see Share Data Within App Designer Apps.
Version History
Introduced in R2016aSetting or getting UIContextMenu property is not recommended. Instead,
use the ContextMenu
property, which accepts the same type of input and behaves the same way as the
UIContextMenu property.
There are no plans to remove the UIContextMenu property, but it is no
longer listed when you call the set, get, or
properties functions on the FunctionContour object.
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)