coder.sameSizeBinaryOp
Description
result = coder.sameSizeBinaryOp(func_handle,u,v)func_handle on the
operands u and v without implicitly expanding them.
The operands must be of the same size because this function does not allow scalar
expansion.
Use coder.sameSizeBinaryOp to disable implicit expansion for a
specific binary operation or function. Disable implicit expansion to avoid automatic size
change of output sizes, additional code generation, and
performance variation. See Generate Code with Implicit Expansion Enabled, Optimize Implicit Expansion in Generated Code and Compatible Array Sizes for Basic Operations.
To disable implicit expansion for binary operations and functions within a specific
function in the generated code, call coder.noImplicitExpansionInFunction within that function.
Examples
Use coder.sameSizeBinaryOp to apply binary operations and functions where implicit expansion is not required.
Using coder.sameSizeBinaryOp ensures that any variable-size operands of compatible sizes are not expanded automatically. The generated code does not include additional code to enable the automatic expansion of the operands.
In this example, the plus function applies the operation with implicit expansion. The coder.sameSizeBinaryOp function applies the operation without implicit expansion.
type addExample.mfunction [out1,out2] = addExample(a,b) out1 = coder.sameSizeBinaryOp(@plus,a,b); out2 = plus(a,b); end
Define the input types.
a_type = coder.typeof(1,[5 1]); b_type = coder.typeof(1,[5 inf]);
Generate code for the function addExample by using this command.
codegen addExample -args {a_type, b_type} -config:lib -report
Code generation successful: View report
Compare Output Sizes
In the code generation report created in the previous step, place your cursor over the two operations.
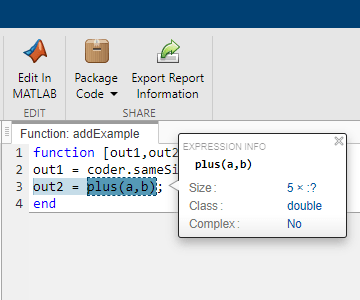
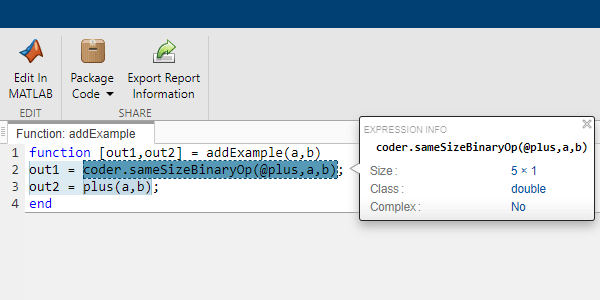
The size of the output from the plus operation is 5x:? whereas the size of the output of coder.sameSizeBinaryOp is 5x1.
The plus function implicitly expands its operands to the output size.
The coder.sameSizeBinaryOp function disables implicit expansion to prevent the automatic expansion of the operands.
Examine the Generated Code
type codegen/lib/addExample/addExample.c/*
* File: addExample.c
*
* MATLAB Coder version : 25.2
* C/C++ source code generated on : 21-Feb-2026 13:28:43
*/
/* Include Files */
#include "addExample.h"
#include "addExample_data.h"
#include "addExample_emxutil.h"
#include "addExample_initialize.h"
#include "addExample_types.h"
#include "omp.h"
#include <emmintrin.h>
/* Function Definitions */
/*
* Arguments : const double a[5]
* const emxArray_real_T *b
* double out1[5]
* emxArray_real_T *out2
* Return Type : void
*/
void addExample(const double a[5], const emxArray_real_T *b, double out1[5],
emxArray_real_T *out2)
{
__m128d r;
__m128d r1;
const double *b_data;
double *out2_data;
int b_loop_ub;
int i;
int i1;
int i2;
int loop_ub;
if (!isInitialized_addExample) {
addExample_initialize();
}
b_data = b->data;
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
out1[i] = a[i] + b_data[i];
}
loop_ub = out2->size[0] * out2->size[1];
out2->size[0] = 5;
b_loop_ub = b->size[1];
out2->size[1] = b->size[1];
emxEnsureCapacity_real_T(out2, loop_ub);
out2_data = out2->data;
loop_ub = b->size[1];
if (b->size[1] < 400) {
for (i1 = 0; i1 < b_loop_ub; i1++) {
_mm_storeu_pd(
&out2_data[5 * i1],
_mm_add_pd(_mm_loadu_pd(&a[0]), _mm_loadu_pd(&b_data[5 * i1])));
loop_ub = 5 * i1 + 2;
_mm_storeu_pd(
&out2_data[loop_ub],
_mm_add_pd(_mm_loadu_pd(&a[2]), _mm_loadu_pd(&b_data[loop_ub])));
loop_ub = 5 * i1 + 4;
out2_data[loop_ub] = a[4] + b_data[loop_ub];
}
} else {
#pragma omp parallel for num_threads(omp_get_max_threads()) private(r, r1, i2)
for (i1 = 0; i1 < loop_ub; i1++) {
_mm_storeu_pd(
&out2_data[5 * i1],
_mm_add_pd(_mm_loadu_pd(&a[0]), _mm_loadu_pd(&b_data[5 * i1])));
r1 = _mm_loadu_pd(&a[2]);
i2 = 5 * i1 + 2;
r = _mm_loadu_pd(&b_data[i2]);
r = _mm_add_pd(r1, r);
_mm_storeu_pd(&out2_data[i2], r);
i2 = 5 * i1 + 4;
out2_data[i2] = a[4] + b_data[i2];
}
}
}
/*
* File trailer for addExample.c
*
* [EOF]
*/
The code generated to calculate out1 by using coder.sameSizeBinaryOp is seen in the first for loop in the function addExample. The code generated to calculate out2 is seen below the first for loop. The generated code for out1 is much smaller, as compared to the code generated to calculate out2.
The code generated for the plus function needs additional code to expand its operands.
This example shows how to generate code for binary operations and functions without implicitly expanding its operands.
The coder.sameSizeBinaryOp function applies the required operation and bypasses additional code generation and change in output size associated with implicit expansion.
This example highlights the difference between the code generated for coder.sameSizeBinaryOp and the code generated for the minus function.
Subtracting Two Operands with Implicit Expansion
For this code snippet, the generated code implicitly expands the output.
type fooImpEx.mfunction out = fooImpEx(a,b) out = b - a; end
Define the operand types.
a = coder.typeof(1,[2 1])
a =
coder.PrimitiveType
2×1 double
Edit Type Object
b = coder.typeof(1,[2 inf])
b =
coder.PrimitiveType
2×:inf double
Edit Type Object
Generate code for the function by running this command:
codegen fooImpEx -config:lib -args {a,b}
Code generation successful.
The code generated for the function fooImpEx is shown here.
type codegen/lib/fooImpEx/fooImpEx.c/*
* File: fooImpEx.c
*
* MATLAB Coder version : 25.2
* C/C++ source code generated on : 21-Feb-2026 13:30:01
*/
/* Include Files */
#include "fooImpEx.h"
#include "fooImpEx_emxutil.h"
#include "fooImpEx_types.h"
#include <emmintrin.h>
/* Function Definitions */
/*
* Arguments : const double a[2]
* const emxArray_real_T *b
* emxArray_real_T *out
* Return Type : void
*/
void fooImpEx(const double a[2], const emxArray_real_T *b, emxArray_real_T *out)
{
const double *b_data;
double *out_data;
int i;
int i1;
int loop_ub;
b_data = b->data;
i = out->size[0] * out->size[1];
out->size[0] = 2;
loop_ub = b->size[1];
out->size[1] = b->size[1];
emxEnsureCapacity_real_T(out, i);
out_data = out->data;
for (i1 = 0; i1 < loop_ub; i1++) {
_mm_storeu_pd(&out_data[2 * i1], _mm_sub_pd(_mm_loadu_pd(&b_data[2 * i1]),
_mm_loadu_pd(&a[0])));
}
}
/*
* File trailer for fooImpEx.c
*
* [EOF]
*/
The generated code includes code to automatically expand the size of compatible operands.
Subtracting Two Same-Size Operands Without Implicit Expansion
This code snippet uses coder.sameSizeBinaryOp to apply the operation without using implicit expansion.
type fooSameSize.mfunction out = fooSameSize(a,b) out = coder.sameSizeBinaryOp(@minus,b,a); end
Generate code for the function by running this command:
codegen fooSameSize -config:lib -args {a,b}
Code generation successful.
The code generated for the function fooImpEx is shown here.
type codegen/lib/fooSameSize/fooSameSize.c/*
* File: fooSameSize.c
*
* MATLAB Coder version : 25.2
* C/C++ source code generated on : 21-Feb-2026 13:30:02
*/
/* Include Files */
#include "fooSameSize.h"
#include "fooSameSize_types.h"
/* Function Definitions */
/*
* Arguments : const double a[2]
* const emxArray_real_T *b
* double out[2]
* Return Type : void
*/
void fooSameSize(const double a[2], const emxArray_real_T *b, double out[2])
{
const double *b_data;
b_data = b->data;
out[0] = b_data[0] - a[0];
out[1] = b_data[1] - a[1];
}
/*
* File trailer for fooSameSize.c
*
* [EOF]
*/
In this case, the variable out is fixed-size and the code generated for the operation applied by the coder.sameSizeBinaryOp function does not expand the operands. The generated function fooSameSize does not contain additional loops to increase the size of the operands.
Input Arguments
Binary function to apply, specified as a function handle,
func_handle must be a binary (two-input) element-wise function of
the form C = func_handle(u,v) that accepts arrays
u and v with the same-size. Apply these binary
functions without implicit expansion by using
coder.sameSizeBinaryOp:
| Function | Symbol | Description |
|---|---|---|
plus | + | Plus |
minus | - | Minus |
times | .* | Array multiply |
rdivide | ./ | Right array divide |
ldivide | .\ | Left array divide |
power | .^ | Array power |
eq | == | Equal |
ne | ~= | Not equal |
gt | > | Greater than |
ge | >= | Greater than equal to |
lt | < | Less than |
le | <= | Less than equal to |
and | & | Element-wise logical AND |
or | | | Element-wise logical OR |
xor | N/A | Logical exclusive OR |
bitand | N/A | Bit-wise AND |
bitor | N/A | Bit-wise OR |
bitxor | N/A | Bit-wise XOR |
max | N/A | Binary maximum |
min | N/A | Binary minimum |
mod | N/A | Modulus after division |
rem | N/A | Remainder after division |
atan2 | N/A | Four-quadrant inverse tangent; result in radians |
atan2d | N/A | Four-quadrant inverse tangent; result in degrees |
hypot | N/A | Square root of sum of squares |
Example: result = coder.sameSizeBinaryOp(@plus, u,
v);
Data Types: function_handle
Input array, specified as scalar, vector, matrix, or multidimensional array. Inputs
u and v must be of the same sizes.
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | logical | char | string | struct | table | cell | function_handle | categorical | datetime | duration | calendarDuration | fi
Complex Number Support: Yes
Input array, specified as scalar, vector, matrix, or multidimensional array. Inputs
u and v must be of the same sizes.
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | logical | char | string | struct | table | cell | function_handle | categorical | datetime | duration | calendarDuration | fi
Complex Number Support: Yes
Version History
Introduced in R2021b
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)